Sticking is a multifactorial problem so that one single “fix” is unlikely to solve it completely, and “solutions” addressing one problem may exacerbate another. A broad-based strategy involving the API, formulation, tablet tooling and the manufacturing process is the most likely to provide robust and lasting solution.
Sticking, an extension of filming, occurs when multiple layers of material adhere to the punch. In this text, we will use sticking to address all the areas where unwanted adherence of material to the punch occurs
The tablet production process has become more simplified and more mechanized with the event of technology. However, the complexity of the tablet punching process has increased. But relatively the issues related to the tablet manufacturing process haven't yet been significantly reduced.
Research has revealed that tablet processing problems are often because of the issues mostly found either within the formulation or within the compression. Sticking is one of the main problems related to tablet manufacturing, and it's because of the wrong addition of excipients or errors within the granulation process.
Sticking in Tablets
Sticking is additionally called filming. Sticking/filming is one of the main problems that tablet manufacturing companies face over and once again. Mostly, tablet sticking occurs when granulated powder sticks to the punch surface causing deformed tablets.
Not only is that the problem costly to the manufacturers but also for the formulators. Sticking is caused by a variety of things including the machines utilized in the tablet manufacturing process.
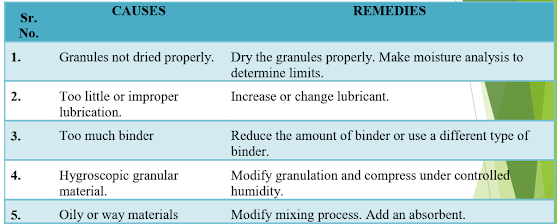
First, sticking is caused especially when the granules aren't dried properly. during this case, the granules should be properly dried before the tablet-making process starts.
In addition, the manufacturers should also assess and analyze the moisture content so as to work out the bounds at which the method is often avoided causing tablet sticking.
Tablet sticking also can be occurred due to either insufficient or improper granule lubrication. during this stage, it's up to the formulator to work out the precise cause and remedy it appropriately. The formulator should add more lubricants if it's acknowledged that tiny lubrication is that the reason why the tablets are sticking. And if the lubricant used is improper, proper oil should be utilized in order to remedy the tablet sticking problem.
In addition, an excessive amount of binder has also been found to be the rationale for tablet sticking within the manufacturing process. during this case, there are two possibilities to remedy the matter. the primary remedy is to scale back the quantity of binder utilized in the manufacturing process. Alternatively, the binder in question also can be changed so on prevent the tablet sticking problem.
Moreover, tablet sticking is additionally mentioned by hygroscopic granular materials. If this is often the explanation for tablet sticking, then the granulation process should be modified and compressed under controlled humidity. Sticking also can flow from to either too soft or weak granules. it's important to optimize the quantity of binder and therefore the granulation technique so as to stop tablet sticking.
Nonetheless, tablet sticking also can be caused by either oily or way materials. The tablet manufacturers should, therefore, modify the blending process so as to stop tablet sticking. additionally, the manufacturers also can add an absorbent to remedy sticking as a result of oily materials.
On the opposite hand, tablet sticking also can be regarding the variety of things that are usually related to the machines in use. Sticking is caused when a machine having too deep concavity for granulation is employed. The concavity should be reduced to the optimum so as to stop tablet sticking. insufficient pressure has also been found to cause tablet sticking. If insufficient pressure is that the problem, then increasing the pressure will help prevent tablet sticking.
It has also been acknowledged that compressing too fast can cause tablet sticking within the manufacturing process. Therefore, the speed at which the granules are compressed should be quite slow but appropriate for the method.
The Causes and Remedies of Sticking related to ‘Formulation’
The Causes and Remedies of Sticking related to ‘Machine’
Conclusion:
Sticking : tablet material adhering to the die wall.
Filming is slow form of sticking and is largely due to excess moisture in the granulation
Reason: improperly dried or improperly lubricated


Comments
Post a Comment